Energy Efficiency in Green Buildings
Energy efficiency in green buildings is a cornerstone of sustainable architecture, focusing on the responsible use of resources to minimize energy consumption while maximizing occupant comfort. By implementing innovative design strategies, advanced technologies, and eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient green buildings aim to reduce their carbon footprint and operating costs. This approach not only addresses environmental concerns but also promotes healthier indoor environments and long-term economic savings. Understanding the fundamentals and benefits of energy efficiency in green buildings is crucial for architects, developers, and building owners committed to creating a more sustainable future.
Sustainable Architectural Design

Passive solar design leverages the natural path of the sun to regulate indoor temperature and reduce reliance on mechanical heating or cooling systems. By orienting a building to capture or deflect solar rays according to seasonal needs, interiors can remain comfortable year-round with minimal energy expenditure. The incorporation of thermal mass materials, such as concrete or brick, allows walls and floors to absorb and store heat during the day and release it gradually at night. This reduces the need for artificial climate control, contributing to significant energy savings over time.
Smart Building Automation
Smart building automation involves integrated networks of sensors, controllers, and software that optimize energy use throughout a building. These systems monitor lighting, heating, cooling, and even occupancy patterns to make real-time adjustments for maximum efficiency. Automated controls ensure that energy is not wasted on empty spaces or suboptimal conditions, significantly lowering overall consumption. As these systems continuously analyze performance data, they can identify inefficiencies and enable facilities managers to make informed decisions, further enhancing energy conservation strategies.
High-Efficiency HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems are typically the largest energy consumers in buildings. By adopting high-efficiency HVAC systems—such as variable refrigerant flow technology, energy recovery ventilators, and advanced heat pumps—green buildings achieve superior climate control with minimal resource input. These systems are designed to operate only when needed and respond dynamically to changing indoor conditions, effectively reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Their integration with smart controls further refines performance, delivering comfort without unnecessary energy expenditure.
Renewable Energy Integration
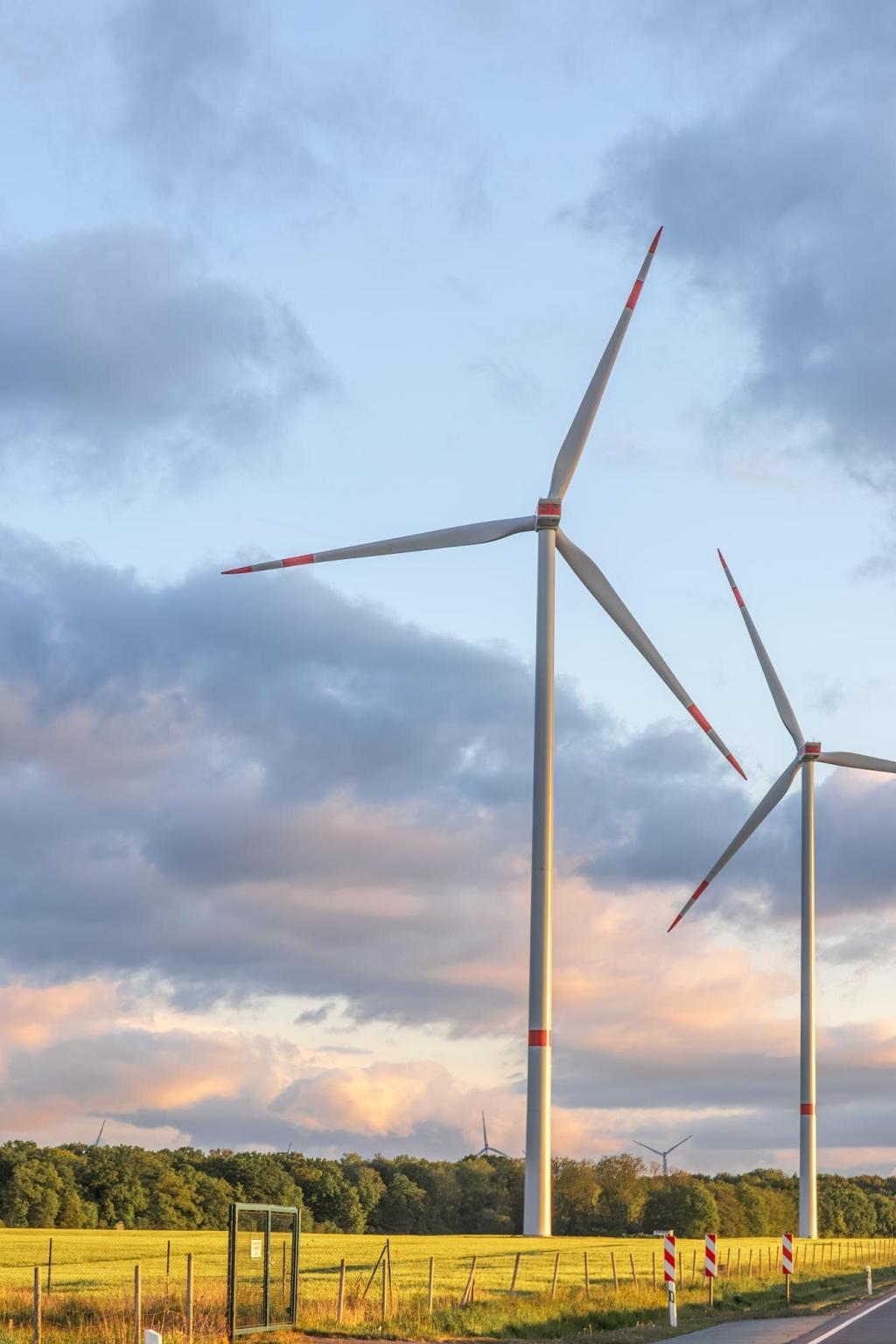
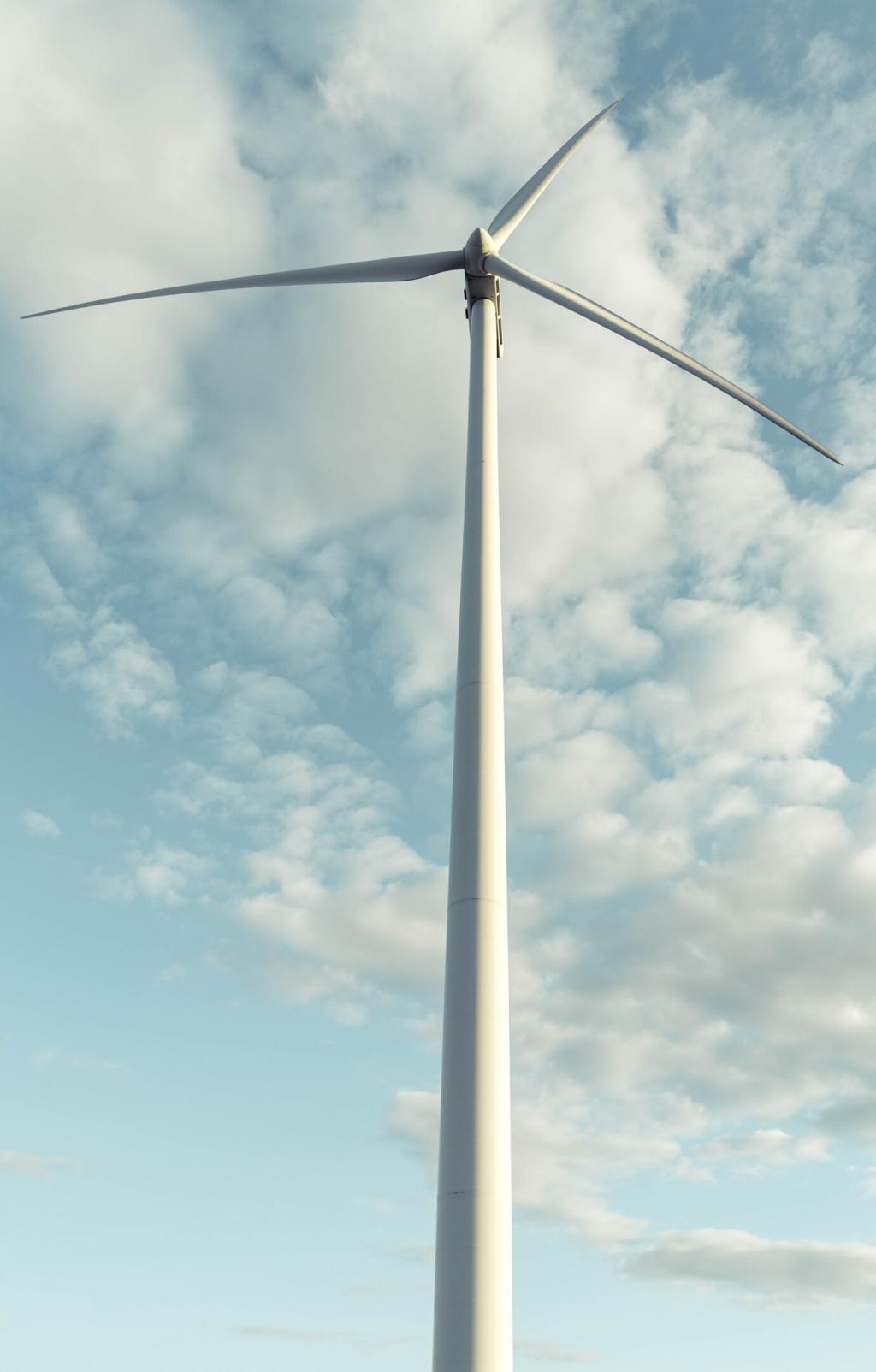
The use of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems, is central to achieving energy efficiency in green buildings. By generating clean energy onsite, buildings decrease their reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Sophisticated energy storage solutions and grid-interactive systems allow for seamless incorporation of renewables, ensuring a consistent and sustainable power supply. As renewable technology advances and becomes more affordable, its integration is increasingly feasible and beneficial for all types of buildings.
Material Selection and Construction Techniques
Low-Emissivity Building Materials
Low-emissivity (low-e) materials are designed to reflect rather than absorb radiant heat, improving a building’s thermal performance. These materials are typically used in windows, roofing, and insulation to impede the transfer of solar heat into interior spaces while retaining wanted warmth during colder months. Low-e coatings on glass, radiant barriers, and advanced insulative foams are examples of such technologies. By effectively managing heat flow, these materials contribute to substantial energy savings and enhance occupant comfort throughout the year.
Modular and Prefabricated Construction
Modular and prefabricated construction methods streamline building processes, reduce material waste, and improve energy efficiency. Components are manufactured offsite in controlled environments, where precision fabrication results in tighter seals and superior insulation. Once assembled onsite, these buildings often exceed conventional standards for airtightness and thermal performance. Additionally, these techniques offer faster construction timelines and greater flexibility in implementing sustainable features, making them an increasingly popular choice in green building design.
Recycled and Renewable Materials
The use of recycled and renewable materials demonstrates a commitment to resource conservation and environmental stewardship. Recycled steel, reclaimed wood, and composite materials made from agricultural waste offer high performance with a lower environmental footprint. Similarly, renewable materials such as bamboo and cork regenerate quickly, reducing the impact on natural resources. By specifying materials that are responsibly sourced and minimally processed, green buildings not only improve energy efficiency during operation but also promote sustainability throughout their entire lifecycle.
Join our mailing list